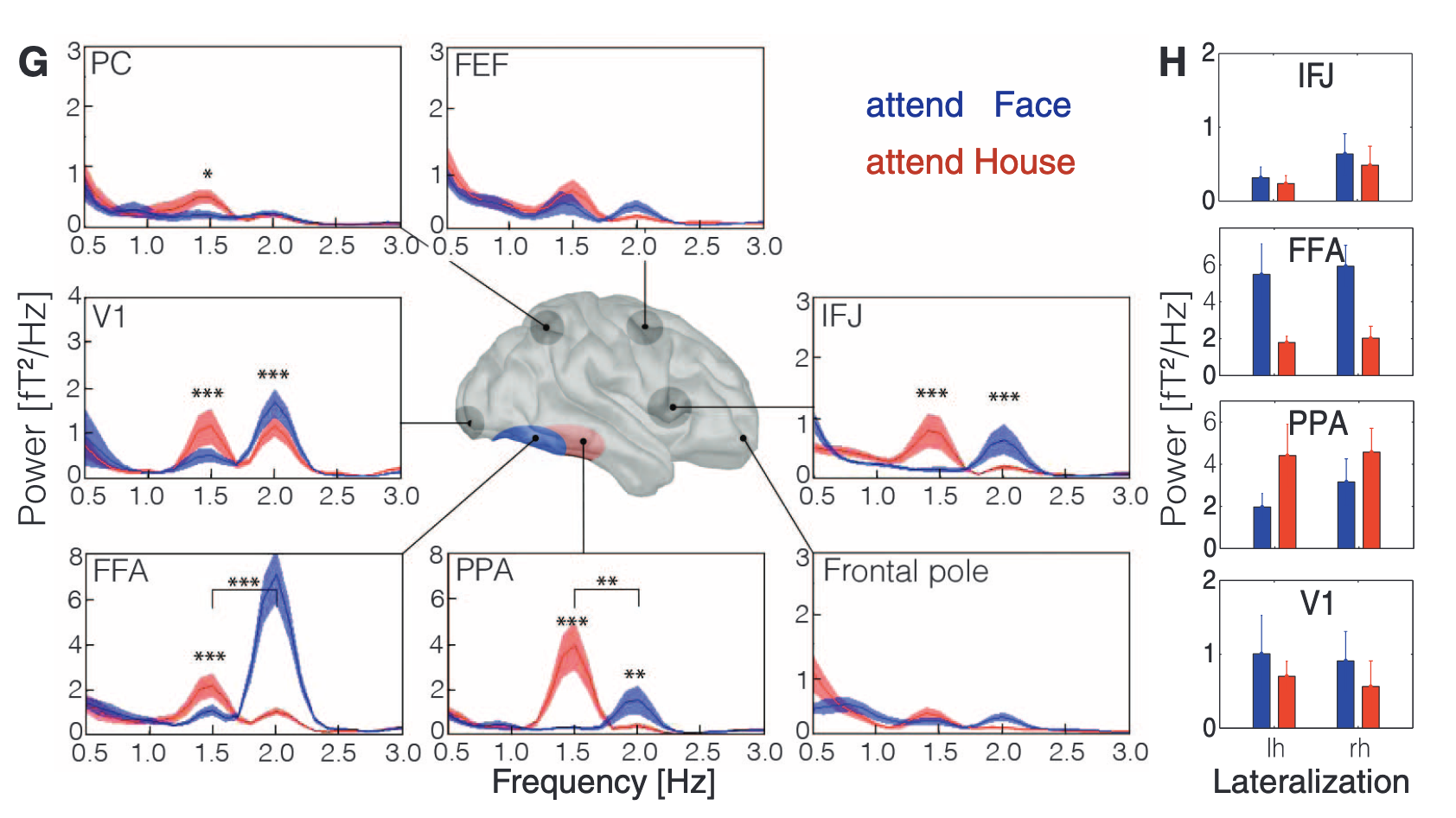
FEF vs IFJ
eine extra Seite, weil das wichtig ist:
- both localized within the same gradient of the rostro-caudal axis. (Bedini & Baldauf (2021))
- FEF and IFJ dynamically interact with subcortical and thalamic structures to achieve efficient control of behaviour (Halassa & Kastner, 2017; White et al., 2017). (Bedini & Baldauf (2021))
- both are involved in top-down attention and show evidence of sustained activity in response to a cue (Bedini & Baldauf (2021))
| FEF | IFJ | |
|---|---|---|
| Domain | where/dorsal/spatial (Bedini (n.d.)) | what/ventral/non-spatial (Bedini (n.d.)) |
| Topography | full map of contralat. space (Bedini & Baldauf (2021)) | - |
| Networks | DAN, cingulo-opercular network (Bedini & Baldauf (2021)) | FPN, language network (Bedini & Baldauf (2021)) |
| SLF | SLF1 + SLF2 (Bedini & Baldauf (2021)) | SLF2 + SLF3 (Bedini & Baldauf (2021)) |
| Function | spatial processing, maintenance of goal-related information, oculomotor control and spatial working memory. (Bedini & Baldauf (2021)) | non-spatial processing, maintenance of goal-related information, may encode higher level of abstraction (Bedini & Baldauf (2021)), more context dependent + influenced by bottom-up factors (Bedini & Baldauf (2021)) |
| Evolution | more ancient dorsal pathways, visiospatial attention systems are evolutionary older and preserved in primates (Bedini & Baldauf (2021)) | more recent evolution due to human behaviours (Bedini & Baldauf (2021)) |
| Subregions | IFJa, IFJp |
see also
Tags: neuroscience science
Superlink: 050 🧠Neuroscience
FEF
IFJ
Auditory Where-Stream (Dorsal)
Auditory What-Stream (Ventral)
Source
Created: 2025-11-19 12:25