basal ganglia
Basal ganglia are (mostly) located between the insular cortex (insula) and the Thalamus. The internal capsule crosses between the different BG structures.
Aufgaben
Die basal ganglia ist zuständig für Gewohnheiten/Habits. Sie ist dafür zuständig, dass wir routinierte Aufgaben ohne nachzudenken richtig machen.
Auch Gebete und Fluche werden durch die basal ganglia ausgeführt.
Das Gehirn lagert gewohnte Tätigkeiten zu den Basal Ganglien aus, um Raum im PFC freizuräumen. Warum?
Um auf unerwartete Dinge schneller reagieren zu können. Wenn wir in einer Tätigkeit voll und ganz drin sind (also unser PFC sehr aktiv ist), haben wir kaum Raum, auf Veränderungen zu reagieren.
aus The Mind
Applying this idea to highway driving, the brain may devote fewer resources while driving on a familiar highway, thus saving processing capacity for unexpected events, like a deer crossing the road.
- Goldstein, E. Bruce. The Mind (S.107-108). MIT Press. Kindle-Version.
other functions
Based on the given context, the key points about the basal ganglia and its functions are as follows:
- The basal ganglia is responsible for habits and routine tasks, allowing us to perform them without conscious effort.
- It plays a role in executing prayers and curses.
- The basal ganglia helps free up space in the prefrontal cortex to respond to unexpected events more quickly.
- It is involved in Reward processing, Motivation, and pleasure experiences.
- The basal ganglia is part of the brain’s reward system and integrates motivational and pleasure-related signals with motor functions.
- It receives dopaminergic projections from the ventral tegmentum (VTA) as part of the mesolimbic dopamine pathway.
- The nucleus accumbens, a component of the basal ganglia, is often referred to as the brain’s pleasure center.
- Oxytocin receptors in the nucleus accumbens suggest its involvement in social behaviors and pair bonding.
- The basal ganglia is involved in movement and action planning.
- It is implicated in various diseases, such as hemiballism, which can cause chaotic and involuntary movements.
- The Cerebellar Cortex contains different types of neurons, including stellate neurons, basket neurons, purkinje neurons, golgi neurons, and granule cells.
- Granule cells are the only excitatory neurons in the cerebellar cortex.
- The cerebellar cortex is organized into highly ordered repeating units called folia, which are organized into three layers: the molecular layer, the purkinje cell layer, and the granule layer.
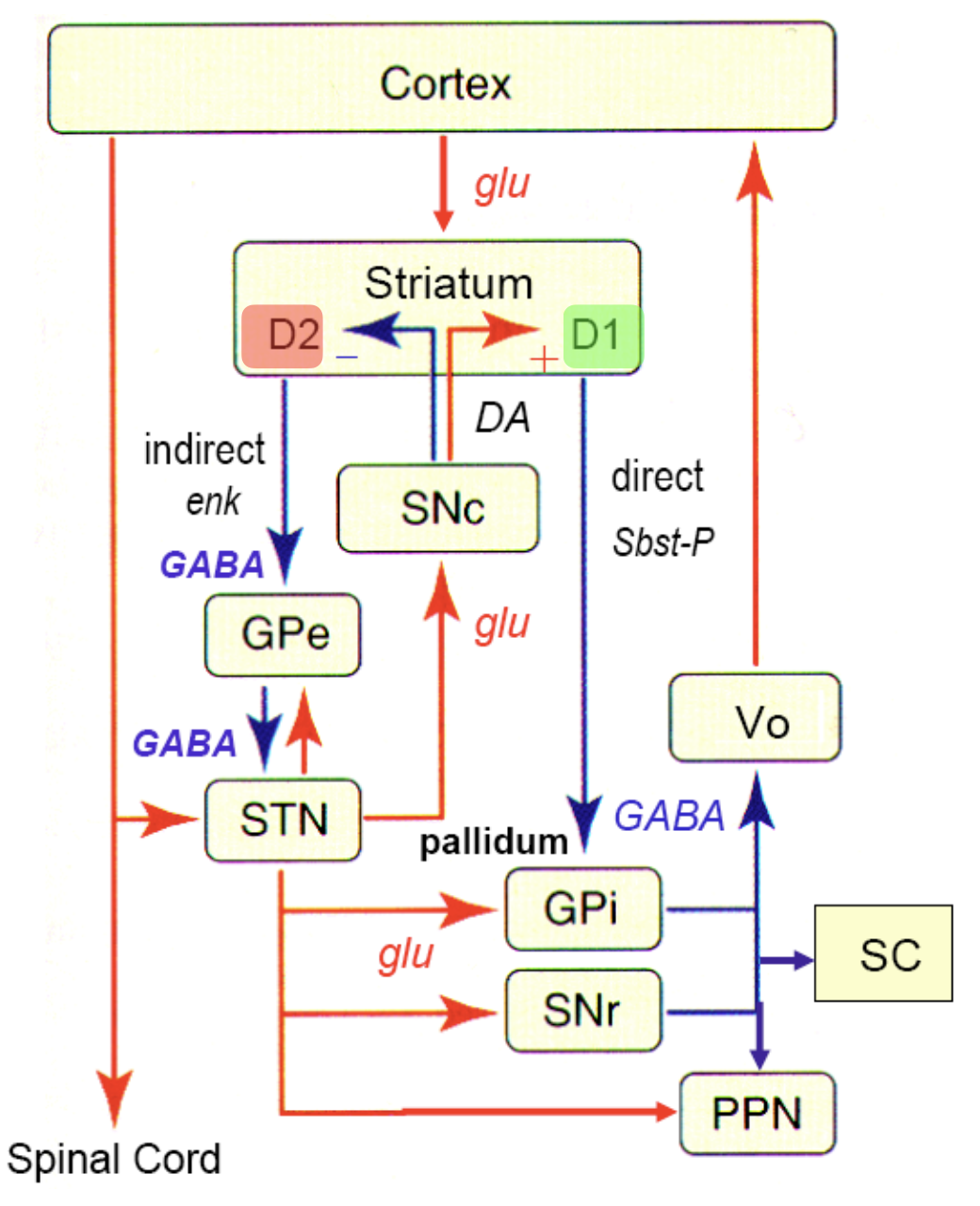
Pathways
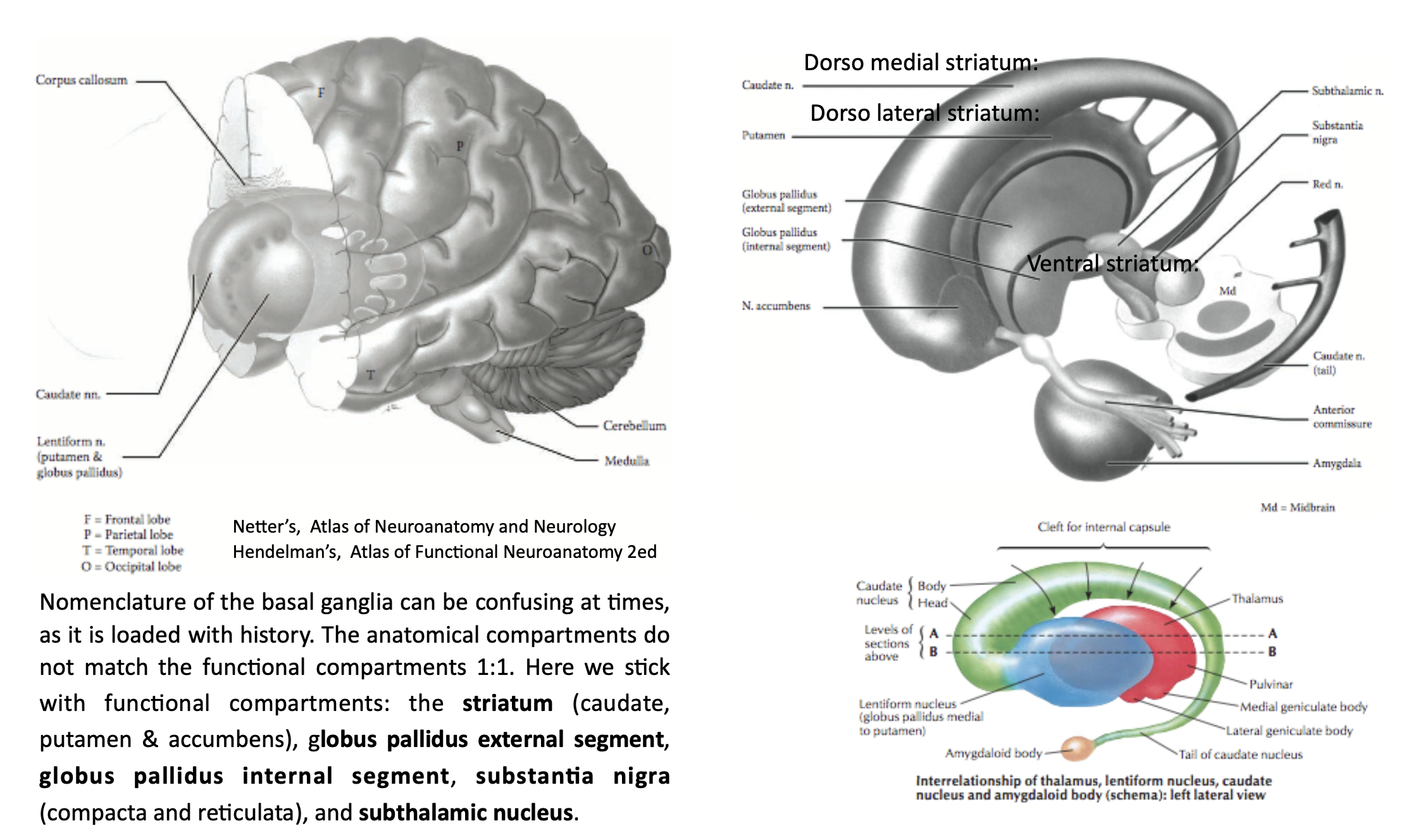
Location
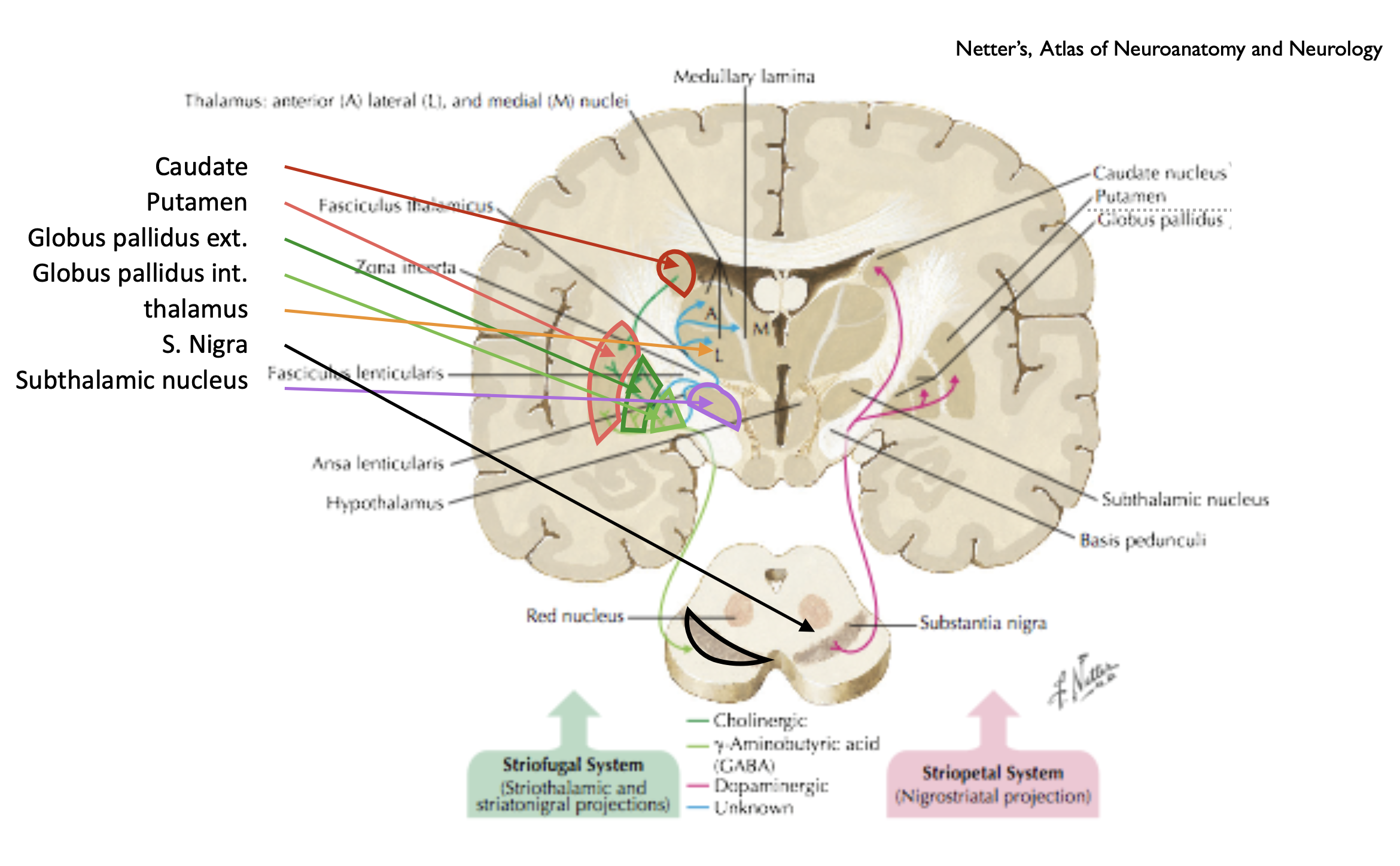
See also
Gewohnheiten für schlechte Zeiten
religions in society
Gewohnheiten schaffen
Selbstbewusstsein durch Gewohnheiten
Status:
Tags: cognitivescience science brainregion
Superlink: 050 🧠Neuroscience
Sources
The Predictive Mind I Perceiving and Acting
Neuroanatomy Import from Anki
what is the role of the nucleus accumbens in the dopamine circuit. give 10 sources
Erstellt: 24-02-22 16:52